HP 5820 (running Comware5 OS) does support fast reroute (FRR) & bidirectional forwarding detection (BFD) feature like Cisco, Juniper and others. Recently I have implemented FRR & BFD with static routes to get route protection/detour to a destination network via different paths on HP5820.
Before come across FRR & BFD – I was looking for a solution that could do tracking of next-hop address in-case of primary link failure and detour the same route through an alternative path using static routes. As the network got multi-vendor devices – a good IGP protocols might not work properly over IPsec VPN tunnel (few latest products does support this although); that’s why I was looking to get this done through static routes. A lot of documents mentioned FRR as a feature of MPLS – this works fine on non-MPLS environment as well.
The next-hope address tracking was done by using BFD (bidirectional forwarding detection) – this is a super fast compared to IGP hello intervals. Default BFD check interval is 50ms. However, BFD is not suitable for slow speed & higher latency network.
Here is the network topology –
In this topology –
a. Primary connectivity between Site-A and Site-B is dark optical fiber link – which provides full wire speed.
b. In case optical fiber fail – the Site-A and Site-B connectivity must go through site to site IPsec VPN over the Internet.
The configurations are following –
a. Site-to-site IPsec VPN been established (omitted)
b. IP address configurations have been done on vlan interfaces on both Site-A & Site-B switches (omitted).
c. Configurations on Site-A HP5820-SW01-
#configure BFD (bidirectional forwarding detection) source to track next-hop IP address
bfd echo-source-ip 172.16.10.1
##define the primary route to Site-B via optical fiber – static route
ip route-static 2.2.2.0 255.255.255.0 Vlan-interface10 172.16.10.2
##define Site-B network prefix to be used in the route policy
ip ip-prefix site-b-prefix 10 permit 2.2.2.0 24
##define route-policy to route to Site-B via IPsec VPN as backup route
route-policy site-a-frr permit node 10
if-match ip-prefix site-b-prefix
apply fast-reroute backup-interface Vlan-interface20 backup-nexthop 172.16.20.2
##configure the backup next hop static route
ip route-static fast-reroute route-policy site-a-frr
d. Configurations on Site-B HP5820-SW02-
#enable BFD (bidirectional forwarding detection) source to track next-hop IP address
bfd echo-source-ip 172.16.10.2
##define the primary route to Site-A via optical fiber
ip route-static 1.1.1.0 255.255.255.0 Vlan-interface10 172.16.10.1
##define Site-B network prefix to be used in route policy
ip ip-prefix site-a-prefix 10 permit 1.1.1.0 24
##define route-policy to route to Site-B via IPsec VPN as backup route
route-policy site-b-frr permit node 10
if-match ip-prefix site-a-prefix
apply fast-reroute backup-interface Vlan-interface30 backup-nexthop 172.16.30.2
##configure the backup next hop static route
ip route-static fast-reroute route-policy site-b-frr
That’s all for the configurations!
Let’s verify the configuration –
#display bfd session ;this will display tracking of next-hop
If the state is DOWN – “backup next-hop” will become the active route
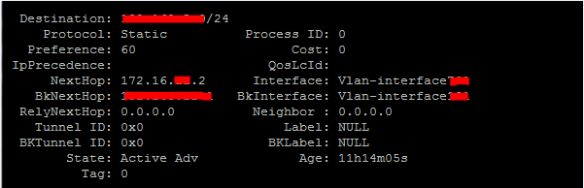
#display ip routing-table 2.2.2.0 verbose ;on HP5820-SW01
#display ip routing-table 1.1.1.0 verbose ;on HP5820-SW02
This will display both NextHop and BackupNextHop for the same destination.